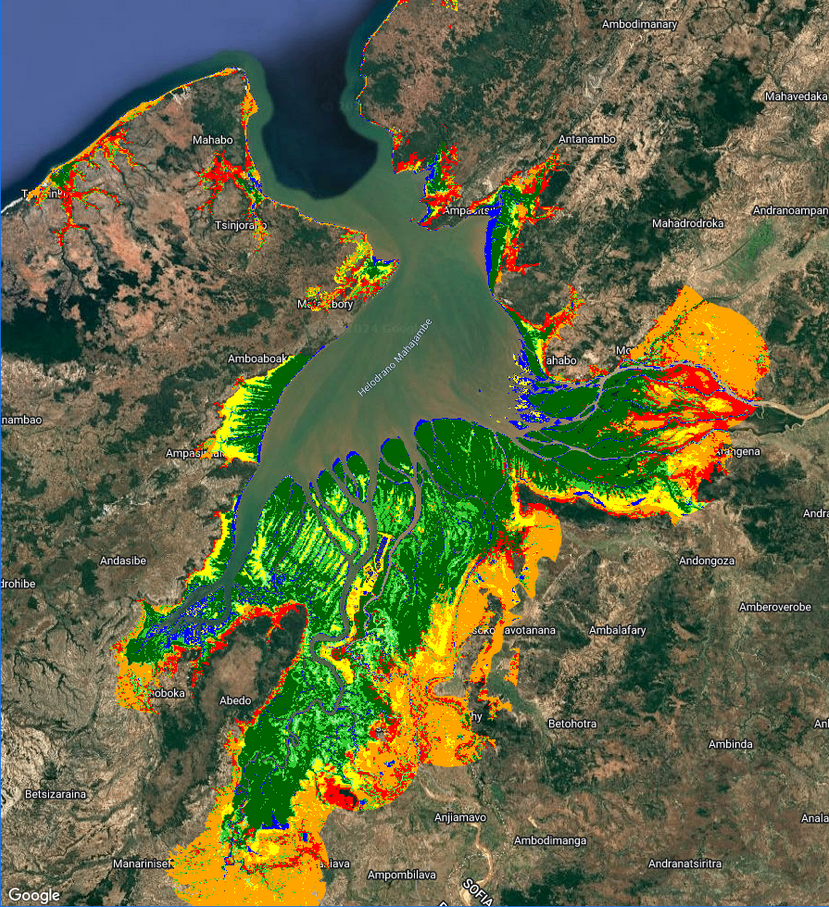
GEM is a mangrove mapping tool freely accessible to non-profit users, built using the powerful cloud computing tool Google Earth Engine (GEE). It is available as both a Desktop tool and an Android App for smartphones and tablets.
The idea for GEM was conceived in 2017 when a gap was identified for a tool that can accurately map mangroves at the local scale, to meet the needs of local mangrove conservation practitioners. Products such as Global Mangrove Watch (first released in 2018) provide excellent mangrove maps for global, regional and national level analysis, but struggle to accurately capture mangrove extent at the local and hyper-local level. Global products often fail to account for local ecological and environmental nuances, leading to maps that are inaccurate or misleading.
GEM not only allows map-makers to account for their local nuances (for example by providing local ground-truthed data), it also utilises state of the art mapping methods such as accounting for tide state. After all, mangroves are a coastal ecosystem, meaning they appear (and are!) vastly different depending on whether the tide is in or out. Mapping using imagery captured at high-tide runs the risk of missing mangroves that are inundated by water, and mapping at random, and therefore variable tide levels across time adds confusion to the mapping process. GEM accounts for all of this by using imagery acquired at consistent tide levels.
Supported and funded by British marine conservation NGO Blue Ventures, the first GEM tool (v1) was released and published in 2020 in the Remote Sensing Journal, where it received an Editor’s Choice Award.